Just like humans, cats are prone to health issues, some of which can be fatal if not treated promptly. While cats are generally good at self-maintenance, it’s important for pet owners to be aware of the signs and symptoms of common cat health problems. Knowing these signs can help you seek veterinary help for your cat and take precautionary measures to prevent further complications. In this article, we’ll discuss five of the most common health problems and illnesses that cats frequently experience.
1. Obesity
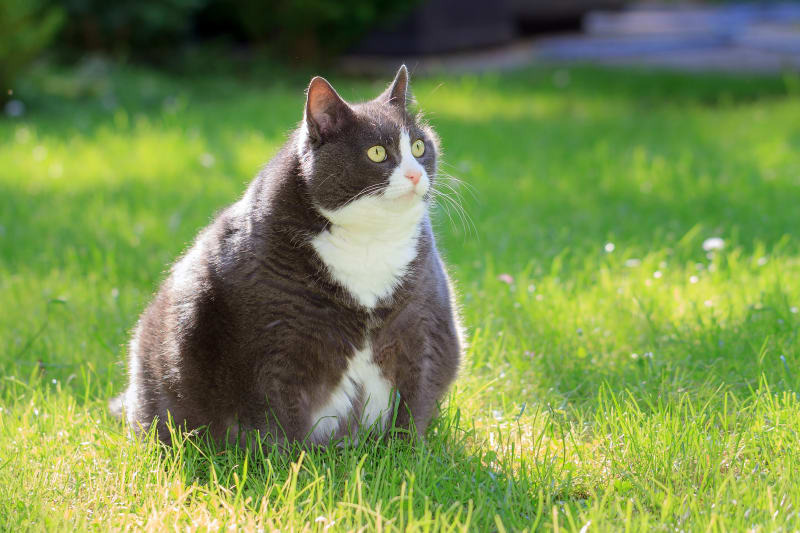

Similar to humans, obesity is a common health issue in cats, with around 30-35% of cats in North America being affected. Almost half of cats aged between 5 to 11 years weigh more than their recommended weight. As a responsible cat owner, it’s easy to assess your cat’s weight to determine if it is overweight or obese.
Cats are considered overweight if their weight is 10-20% above their standard body weight, while a weight that exceeds 20% or more than their ideal body weight is classified as obese. One way to assess your cat’s weight is by feeling its backbone and ribs; if it’s challenging to touch these areas, your cat may be overweight or obese. Consult your veterinarian to obtain the ideal body weight chart for your cat.
Cats are considered overweight if their weight is 10-20% above their standard body weight, while a weight that exceeds 20% or more than their ideal body weight is classified as obese. One way to assess your cat’s weight is by feeling its backbone and ribs; if it’s challenging to touch these areas, your cat may be overweight or obese. Consult your veterinarian to obtain the ideal body weight chart for your cat.
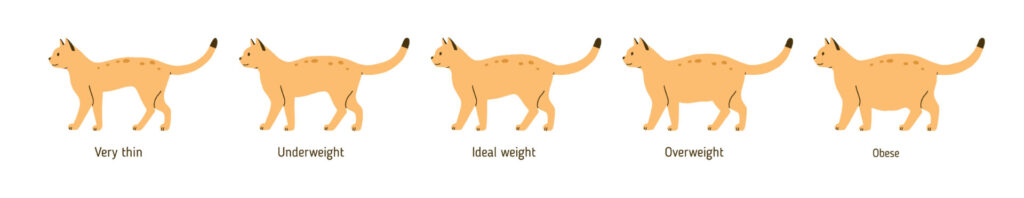
How to Prevent Obesity
- Ask your vet to suggest the most suitable food for your cat based on their age, breed, and overall health status.
- Incorporate more physical activity into your cat’s daily routine and use interactive feeding toys that encourage them to engage in play.
- Limit the number of treats you give your cat to prevent excessive weight gain and health issues.
- Schedule regular veterinary check-ups for your cat to ensure optimal health and wellness.
2. Worms

Worms are internal parasites that can be harmful to both kittens and older cats, regardless of whether they live indoors or outdoors. Intestinal parasites such as roundworms, hookworms, tapeworms, and ringworms are prevalent among cats. Failure to provide regular preventive healthcare for your cats can result in a variety of symptoms, including a distended abdomen, lack of appetite, diarrhoea, vomiting, etc.
Prevention of Worms in Cat
- Avoid exposing your cat to stray or outdoor cats, rodents, fleas, and their feces.
- Ensure a flea-free environment by treating your pet, their bedding, home, and yard regularly.
- Maintain good hygiene when handling your cat’s litter and waste by disposing of it in an appropriate location.
- Follow a regular deworming schedule and seek advice from your vet.
3. Dental Disease
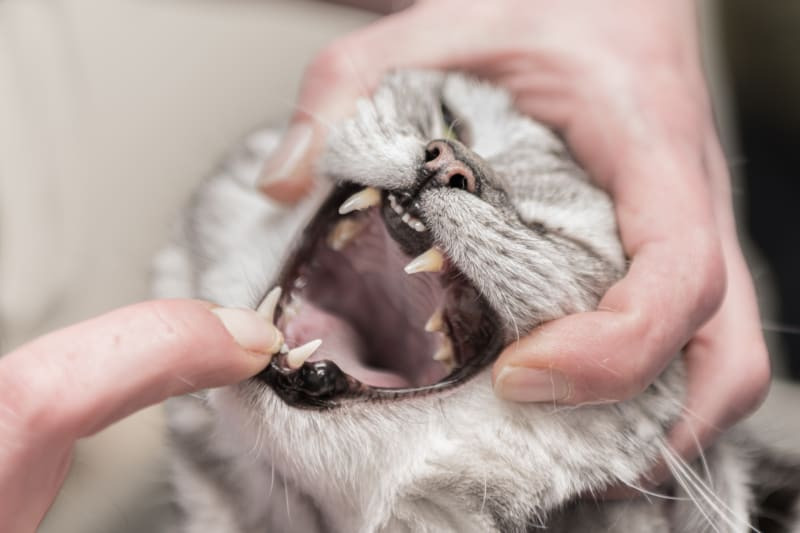
Periodontal diseases, including gingivitis, periodontitis, and tooth resorption, are common in cats, especially among senior cats over four years old. Approximately 50% of senior cats suffer from dental diseases that cause inflammation and pain in the gums. This inflammation is caused by the gradual build-up of plaque, a bacterial growth on the teeth, that if left untreated can turn into dental tartar. Dental tartar, a difficult-to-remove deposit that appears yellow or brown, can lead to serious infections around the teeth of your pet.
Prevention of Dental Disease
- A combination of dry and canned food is recommended for your cat, as the dry food can aid in cleaning their teeth.
- To prevent additional dental issues, it’s crucial to clean your cat’s teeth on a weekly basis.
- Regular veterinary check-ups are necessary to ensure the health and well-being of your cat, so always consult with your veterinarian.
4. Feline Lower Urinary Tract Diseases
According to some estimates, up to 3% of cats seen by veterinarians suffer from feline lower urinary tract disease (FLUTD), which encompasses a group of feline diseases with various causes. FLUTD symptoms include depression, dehydration, lack of appetite, vomiting, etc.
Prevention of Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease
- Keep your cat at a healthy bodyweight.
- Ensure that your cat consumes an adequate amount of water each day.
- Regularly engage your cat in physical activity through play or exercise.
- Provide a stress-free environment to promote optimal mental health for your cat.
Finally, as a responsible cat owner, it’s important to be aware of the common health issues mentioned above and seek immediate veterinary attention if you notice any symptoms in your cat, to ensure early treatment and proper care.
